UX designer vs UI designer vs Product Designer vs UX researcher
Sector: UI/UX
Author: Nisarg Mehta
Date Published: 09/12/2022

Generally, there is a lot of confusion about the different UX disciplines and how companies list job roles.
Even some recruiters don’t understand the difference between UX designer, UI designer, product designer, and UX researcher, so they post a job for a UX designer when in reality, the job description might be for a product designer or researcher.
To eliminate this information gap, here we’re explaining the four most common job titles in the user experience design area.
So without further ado, let’s get started with the first one.
1. UX Designers
It’s crucial for you to comprehend what UX design really is before you know what a UX designer is and does.
UX design centers on the connection between real human users (you and me) and everyday goods and services like websites, apps, and coffee machines. It blends aspects of psychology, business, market research, design, and technology, among other things.
Here, the UX designer works on every aspect of a product’s development, including design, usability, function, branding, and marketing. Their work covers the entire end-to-end journey a user takes with a product, including finding new opportunities for the product and company.
The UX designer’s job is to create something that is functional, engaging, and accessible. Although the procedure varies from product to product and company to company, there are typically the same phases of development.
UX Designers’ Roles and Responsibilities
As user experience designers, they are responsible for the user’s satisfaction with a product. UX designers view themselves as the customers’ advocate, constantly searching for ways to improve their experience.
Let’s examine some of the duties and tasks that UX designers might confront throughout the design process.
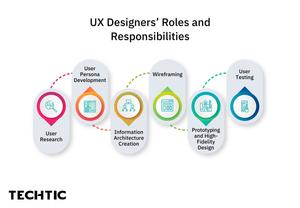
User Research
Many UX designers aren’t aware of how much research UX design requires. Yet, research is critical to understanding the user and their unique demands, as it is a key component of UX design.
User research is frequently used to determine how consumers behave, what motivates them, and what they want in order to determine what opportunities exist for product solutions in a particular market.
Data collection, surveys, user interviews, and focus groups are among the research methods most frequently used by UX designers to obtain information and insights about their target audience.
User Persona Development
Constructing user personas is another critical phase of the UX design process. From their findings, UX designers identify patterns and similarities to create personas representing their user base.
UX developers require demographic information, motivations, needs, potential responses, and everything else mentioned to create a product that suits the user persona. User personas assist the organization in understanding who they’re serving.
Information Architecture Creation
The structure of a website, app, or other product is referred to as information architecture. According to Adobe, IA is ‘the construction of a structure for a website, app, or other product that enables users to locate the information they desire.’
The design team begins by designing wireframes and prototypes once they have determined how users interact with and navigate through the product or site.
Wireframing
UX Designers create wireframes as one of the first steps toward building the final product.
Wireframes are low-fidelity design sketches that represent different screens or phases of the user experience. In addition, wireframes include simple representations of UI design elements, which serve as a foundation for future development and product design.
Prototyping and High-Fidelity Design
A prototype is a higher-fidelity product version than a wireframe, allowing UX designers to test it and present it to the development team. A clickable prototype allows UX designers to test out different practical variations of an experience and identify areas for improvement.
User Testing
User testing is one form of product testing in which participants are given a chance to interact with a final design prototype to examine its accessibility, usability, and elegance.
Focus groups, moderated user tests, and unmoderated user tests are all examples of other methods. It’s one of the last crucial steps in identifying what adjustments need to be made as you continue with product development.
Skills Required to Become a UX Designer
A successful product or service is one that is brought to market using a wide range of technical and workplace skills (or one that improves on an existing product). Even if you’re new to UX design, you’ve probably already developed a few of these skills.
As a result, you should focus on these critical ones to establish a strong foundation for your career:
Workplace Skills
- Communication skills
- Empathy
- Critical thinking
- Collaboration
Technical Skills
- Research
- Information Architecture
- Prototyping
- Wireframing
2. UX Researchers
UX research aims to learn what end users need and want from a system or product, then use that information to improve the design process for products, services, or software.
The research can vary based on the subject matter. For example, for product teams, UX research might involve validating ideas and prototypes, while for marketing teams, it might involve assessing brand messaging and designs prior to releasing products.
A UX researcher studies user behavior, needs, and motivations in order to make products, services, and websites more intuitive and enjoyable for users.
These researchers utilize quantitative and qualitative research methods to gather extensive data and disseminate it to UX designers. The UX researcher’s objective is to make the design process more efficient and productive.
UX Researchers Roles and Responsibilities

Following are the roles and responsibilities taken care of by UX researchers:
Research Planning and Recruitment
The UX researchers are responsible for developing a well-crafted research plan. They also write research screeners and discussion guides for the participants. Recruiting the participants is also a part of UX researchers’ roles.
Data Collection
Moderating one-on-one usability sessions and helping develop and implement qualitative surveys. The UX researchers also conduct stakeholder and customer interviews to gain more depth in their research.
Data Analysis
Using web instruments to extract insights about user behaviours. Also, to convert user insights into actionable recommendations for the UI/UX and product designing team.
Presentation of Insights
The UX researchers present the findings as per the user personas and information radiators (i.e., journey maps) to communicate the recommendations.
Strategy
UX researchers work very closely with the product teams to formulate research objectives and establish and implement an overall research strategy.
Skills Required to Become a UX Researcher
A UX researcher needs to have the following skills:
- Degree in design research
- Have experience conducting user research
- Understanding of UI design
- Experience with qualitative as well as user-centred design methodologies
- Knowledge of statistics, quantitative methodology, and behavioural analysis
- Critical thinking
- Problem-solving skills
- Collaboration, teamwork, and time-management
- Communication skills
3. UI Designers
As UI design is a subset of UX design, UI design professionals work closely with UX designers to develop and design interactive elements for a project.
An outsider to the profession would be unaware that UI and UX design are distinct professions, as they are frequently used synonymously. Even though they both strive to deliver a pleasant user experience, UX design is a separate phase of the process and is significant in its own right.
UI designers are responsible for designing all the mobile/web app or website screens that make up a digital user interface. They also have to take care of screen layout and individual elements featured on the screens.
UI Designers Roles and Responsibilities
A UI designer may be responsible for a range of different tasks and responsibilities when working day-to-day. These may include competitors’ design analysis, hands-on design work, and the development of overarching design guidelines, among others.

Here we’re listing some roles and responsibilities for a UI designer:
User Research
Collaborating with UX designers to conduct user research and analysis of existing designs to understand user needs and product goals, or working independently to do so.
Competitors’ Design Analysis
Understanding how users expect a product to look and behave based on their experience with similar products by conducting a competitor analysis is how users might expect the product to look and behave.
Elements Designing and Interactive Design
Designing logos and individual UI elements such as buttons, icons, and forms are just one aspect of typography and colour palettes.
Also, creating the interactive properties of different UI elements. For example: creating animations or establishing what happens when a user clicks a certain button.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Designing wireframes and prototypes to foreshadow the UI’s appearance and function before development has started. Also, communicate the wireframes or prototypes to the developers.
Lastly, the UI designers also need to create and maintain a UI style guide for the particular product/website for design consistency.
Skills Required to Become a UI Designer
Sure, being a UI designer requires an eye for detail—but it is so much more than simply sitting in front of a computer screen. UX designers are most successful in a group setting if they have excellent people skills—technological expertise and method are equally critical.
The following skills are necessary for UI designers:
Soft Skills
- Communication
- Collaboration
- Empathy
- Attention to detail
Hard Skills
- Good command over design and prototyping tools such as Sketch, AdobeXD, InVision, Figma etc.
- Strong Foundation of Design Knowledge and Principal including Branding, Typography, Colour theory
- UI design patterns, interaction flows, and design planning
4. Product Designers
A product designer is responsible for the conception and development of a product or service. They may brainstorm solutions to existing issues, connect designers, scientists, and engineers, and help create mockups using wireframes and prototypes.
Product designers comprehend the larger goal of the product while being mindful of the details needed to accomplish it.
However, companies often employ a product designer to play a variety of roles, including user experience designer, customer experience architect, user interface designer, interaction designer, or information architect.
The individual’s area of expertise may vary depending on the company’s size and diversity, as well as the design department’s size and diversity.
Product Designers Roles and Responsibilities
The job roles and responsibilities of a product designer include but are not limited to:
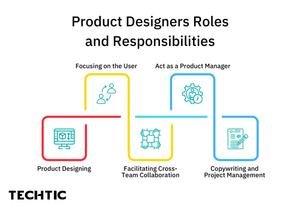
Product Designing
Product designers may wear many hats, but their primary responsibility is still design. A product is created by a product designer using color, typography, detail, and other design elements.
Focusing on the User
In general, a product designer will fold UX principles into their design. For example, product designers may conduct A/B testing, email surveys, and other UX research, build wireframes, prototypes, and journey maps, or know how to do so.
Facilitating Cross-Team Collaboration
A product designer who takes a comprehensive approach to developing a product usually works with designers, researchers, and company teams.
Working together ensures that the finished product aligns with the company’s objectives and incorporates all the elements required to produce an effective and well-designed product.
Act as a Product Manager
Understanding the product purpose, doing competitive research, building the feedback synthesis process, and driving product roadmaps and priorities are among the different roles the product designer plays.
Being the acting product managers, they also have to understand the need-value delivery gap and talk to customers to gain more insights.
Copywriting and Project Management
The product designer has to wear different hats, which include working as a project manager and performing duties like copywriting if required.
Skills Required to Become a Product Designer
The following are the skills one should gain to become a successful product designer:
- User interface
- User experience
- Understanding of visual design tools
- Typography
- Color theory
- Project management and leadership experience
- Problem-solving skills
- Eye for aesthetic design and customer appeal
However, Everything is About UX
All of these jobs are part of the UX family, yet they all have distinct jobs and responsibilities. Whether you prefer a generalist and know all of them or a specialist and know only one is up to you.
Be it any case, the best place to start is to gain a solid grasp of UX principles because that’s where it all starts.
UX designing is an inseparable part of product development and marketing. Being the leading UI/UX development company, Techtic focuses on understanding the target audience and the brand image before jumping on to the designing part.



